SCIENCE: EARTH OBSERVATION TECHNOLOGY CONVERTING COMPLEX INFORMATION INTO ACTIONABLE INNOVATIONS FOR CLIMATE RESILIENCE
IMAGE: WeForum.org
A White Paper produced by World Economic Forum and USA MIT Media Lab, examines how integrating complementary technologies with EO data converts complex information into actionable climate insights.
Reproduced under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License
By 2032, satellite Earth observation is projected to produce over 2 exabytes (2 billion gigabytes) of data – transforming Earth observation data into valuable climate and weather information that can be seamlessly integrated into operational decision-making processes. By democratizing climate data of accessibility and cross-sector collaboration, the integration of EO insights into decision-making processes, driving innovation, enabling timely climate action, and supporting global resilience efforts.
Businesses can harness these benefits to develop innovative solutions, increase asset efficiency and better manage financial risks, all leading to increased competitive advantage.
Because physical infrastructure and natural phenomena are at the core of many organizations’ business models, EO applications can be found in nearly every industry, sector and region. Tech-ready industries have the potential to grow EO data’s value the fastest, whereas traditional industries have the most value to gain overall.
Six key industries are responsible for 94% of Earth observation’s total value possible by 2030.
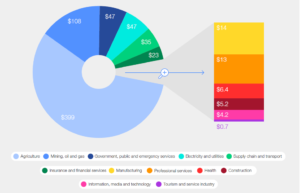
Potential global economic value from EO data, by industry, in 2030 ($, billions).Image: Deloitte/World Economic Forum
According to a new study by the World Economic Forum, in collaboration with Deloitte — Amplifying the Global Value of Earth Observation — the potential value-added from Earth data is estimated to reach $700 billion in 2030 with a cumulative $3.8 trillion contribution to global gross domestic product (GDP) between 2023-2030. At the same time, EO can inform interventions that stand to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by more than 2 billion Gt of CO2 equivalent annually.

EO found in nearly every industry, sector and region, tech-ready industries have the potential to grow EO data’s value the fastest, whereas traditional industries have the most value to gain overall.
1. Agriculture
Earth observation (EO) data has diverse applications in agriculture, including cropping, fisheries, livestock, and timber. Modern techniques increasingly rely on remote sensing and in-situ data to optimize input usage and harvest timing. This approach can also reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from fertilizers by up to 27 million tonnes annually.
2. Electricity and Utilities
Early adopters of EO in the energy and utilities sector have gained a significant information advantage, from site selection to managing transmission infrastructure. EO applications for renewables, such as forecasting energy potential for new solar, wind, and hydropower sites, are crucial for the expected growth of renewable energy this decade.
3. Government, Public, and Emergency Services
Initially led by government initiatives, EO applications for public and emergency services are well-established. Accurate hazard modeling and near real-time monitoring of structures, land, and vegetation enhance disaster preparedness and response. As natural disasters like floods, droughts, wildfires, and hurricanes become more frequent, EO is vital for protecting lives and assets. In wildfire management, early warning systems can help prevent up to 64 million tonnes of GHG emissions annually.
4. Insurance and Financial Services
Insurance companies leverage EO data to better assess risks, offer parametric insurance products, and streamline claims assessments. EO technology also supports sustainable finance by enabling independent verification of sustainable practices. Given the material risks posed by biodiversity loss and climate change, the financial and insurance sectors use EO data to better manage their exposure.
5. Mining, Oil, and Gas
EO data is invaluable for remotely monitoring oil and gas extraction and transmission, offering both economic and environmental benefits. Specialized sensors can predict potential damage and quickly detect leaks, allowing for rapid remediation. This not only prevents product losses but also reduces GHG emissions by up to 1.7 gigatonnes annually. The International Energy Agency estimates that EO can help oil and gas companies cut nearly 45% of methane emissions from operations at no net cost.
6. Supply Chain and Transportation
EO provides traceable supply chain insights for companies focused on ethical sourcing. Businesses can track physical goods within their downstream supply chain operations and upstream in their vendors’ supply chains. As consumer and regulatory pressure for ethical sourcing increases, EO offers a valuable tool for planning interventions and providing objective evidence of their success.












